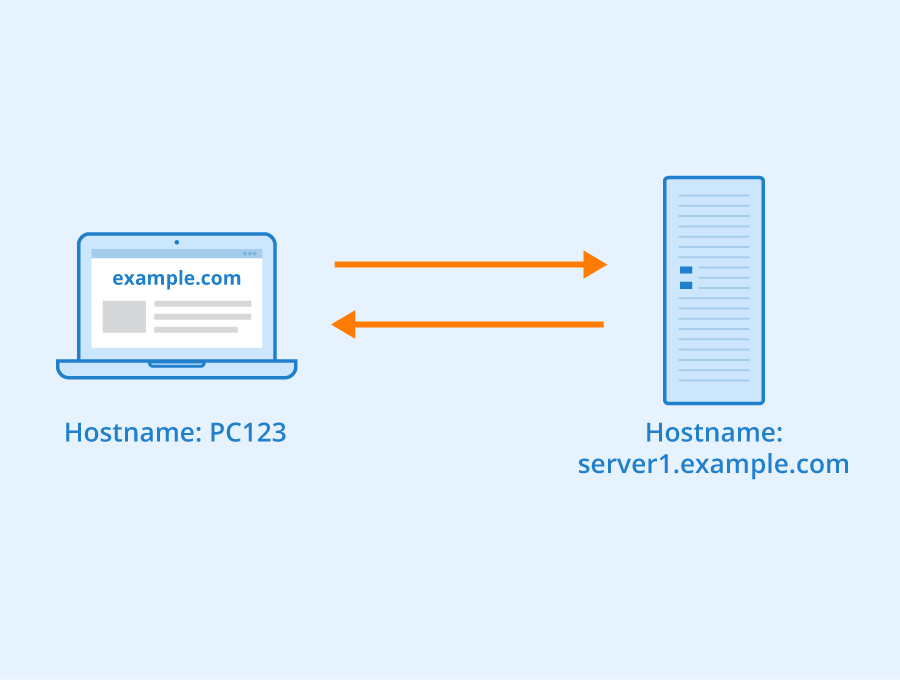
A web server is an example of a host. It is a server that delivers web content to clients over the internet. The web server hosts websites, applications, and other online content, making them accessible to users. It processes requests from clients and sends back the requested information. A web server is an essential component of the hosting infrastructure, allowing websites to be stored and accessed online. It provides the necessary resources and services to ensure the smooth functioning of websites.
A web server is indeed an example of a host, playing a crucial role in the functioning of websites and the internet as a whole. It serves as a foundation for hosting and delivering web content to users, acting as a mediator between the website and the user’s device. With its ability to store and distribute files, handle user requests, and facilitate communication between different components, a web server serves as a vital piece of infrastructure in the digital world.
When we talk about web servers, it’s important to highlight their history and evolution. Early web servers like the CERN HTTPd, released in 1990, paved the way for the modern web servers we use today. Today, popular web server software such as Apache, NGINX, and Microsoft IIS power millions of websites worldwide. With the growing demand for online content and the need for faster and more reliable delivery, web servers continue to evolve and improve, adapting to the ever-changing demands of the digital landscape.
Understanding Web Server and Host
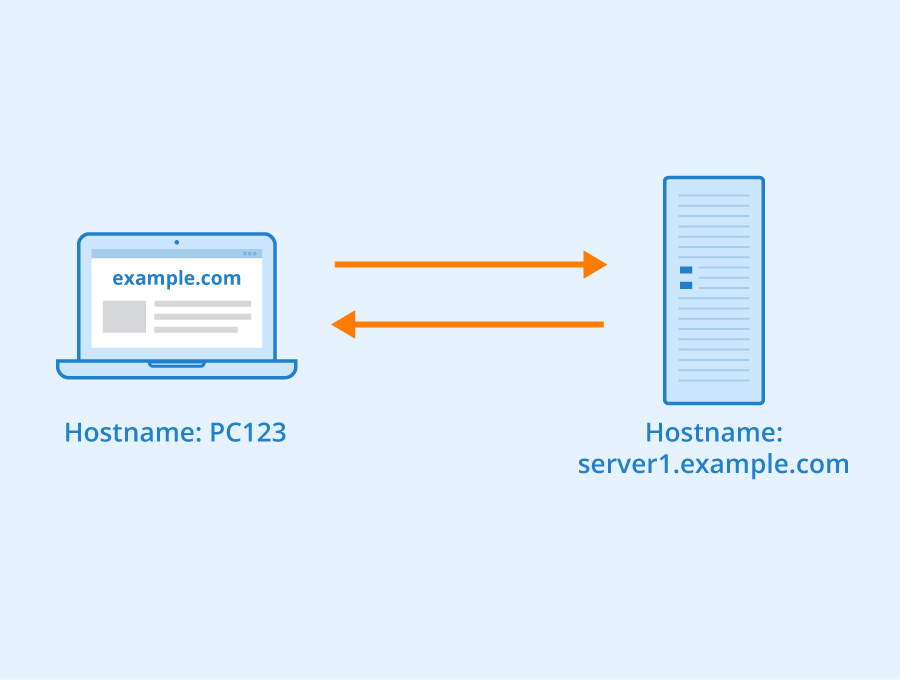
A web server and a host are two different concepts in the world of technology. While they are closely related, it is important to understand the distinction between the two. A web server is a software or hardware that delivers content to users over the internet. It is responsible for receiving and responding to requests from clients (such as web browsers) by serving web pages, files, and other resources. On the other hand, a host refers to a computer or a network that stores and serves data to users or clients.
Now, the question arises: is a web server an example of a host? The answer is both yes and no, depending on the context. In some cases, a web server can be considered a host because it stores and serves web pages and other resources. However, it is important to note that a host can also refer to other types of servers, such as email servers, database servers, or file servers. Therefore, while a web server can be an example of a host, it is not the only type of host that exists.
When discussing whether a web server is an example of a host, it is essential to consider the broader definition of a host, which encompasses various types of servers and networks. By understanding the relationship between a web server and a host, we can gain a deeper insight into the functioning of the internet and the role of different components in delivering content to users.
Different Types of Hosts
As mentioned earlier, a host can refer to various types of servers and networks. In addition to web servers, here are some examples of different types of hosts:
- Email Servers: These hosts are responsible for sending, receiving, and storing email messages. They use protocols such as SMTP, POP, or IMAP to handle email communications.
- Database Servers: These hosts store and manage databases. They are used to store structured data and allow for efficient retrieval and manipulation of data. Examples include MySQL, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server.
- File Servers: These hosts store and manage files that can be accessed by clients over a network. They enable file sharing and collaboration among users.
- Game Servers: These hosts facilitate online gaming by storing and managing game data and facilitating communication between players.
- Domain Name Servers (DNS): These hosts translate domain names (such as example.com) into IP addresses, allowing clients to access websites using human-readable names.
These are just a few examples of the different types of hosts that exist. Each type of host serves a specific purpose and plays a critical role in managing and delivering data or services to clients or users.
Web Server as a Type of Host
Now, let’s delve deeper into the relationship between a web server and a host. In the context of a web server, it can be considered a type of host because it stores and serves web pages and other web resources. A web server receives requests from clients (such as web browsers) and responds by delivering the requested content. It manages the processing of HTTP requests and the delivery of HTTP responses.
When a user types a URL into a web browser (e.g., www.example.com), the browser sends a request to the web server associated with that domain. The web server then retrieves the requested web page and sends it back to the user’s browser, which renders and displays the content. In this scenario, the web server acts as both a host and a server, storing and serving the requested web page.
Web servers can also handle other types of web resources, such as images, videos, CSS files, JavaScript files, and more. They play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth delivery of web content to users across the internet.
Other Types of Hosts
While a web server can be considered a type of host, it is important to note that not all hosts are web servers. As discussed earlier, there are various other types of hosts that serve different purposes. For example:
- Email servers, such as Microsoft Exchange or Gmail’s email infrastructure, handle the storage and delivery of email messages.
- Database servers, like Oracle Database or MongoDB, store and manage structured data for various applications.
- File servers, such as Windows File Server or NAS (Network-Attached Storage), store and manage files that can be accessed by users over a network.
These examples illustrate that while a web server can be considered a type of host, it is not the only type of host that exists. Different types of hosts fulfill specific roles and are designed to handle different types of data and services.
Conclusion
The relationship between a web server and a host is complex but interconnected. While a web server can be considered a type of host because it stores and serves web pages and resources, it is important to recognize that hosts can encompass various other types of servers and networks as well. Different types of hosts, such as email servers, database servers, file servers, and game servers, serve specific purposes and play critical roles in managing and delivering data or services to clients or users.
By understanding the different types of hosts and their functions, we can gain a deeper insight into the infrastructure of the internet and how data is stored and delivered. Whether it’s a web server or another type of host, each plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth operation of various online services and applications.
To dive deeper into the world of web servers and hosts, you can explore additional resources and articles on web servers and hosts. These resources will provide you with in-depth knowledge and a better understanding of the complexities involved in serving content over the internet.
Key Takeaways
- A web server is an example of a host that stores and delivers websites and web applications.
- Web servers host websites and make them accessible to users over the internet.
- Web servers can handle requests from multiple users simultaneously.
- Web servers ensure the secure and efficient delivery of web content.
- Examples of web server software include Apache, Nginx, and Microsoft IIS.
A web server is an example of a host, as it provides a place where websites and web applications can be stored and accessed by users.
Web servers deliver web pages to browsers through the internet, allowing users to view content and interact with websites. They play a crucial role in managing and serving web content to users around the world.